- By Admin
- In Health and Tips,
- Posted July 05, 2024
Blood Clot in Brain: Risks, Symptoms, Prevention & Treatment
What is Blood Clot in Brain?
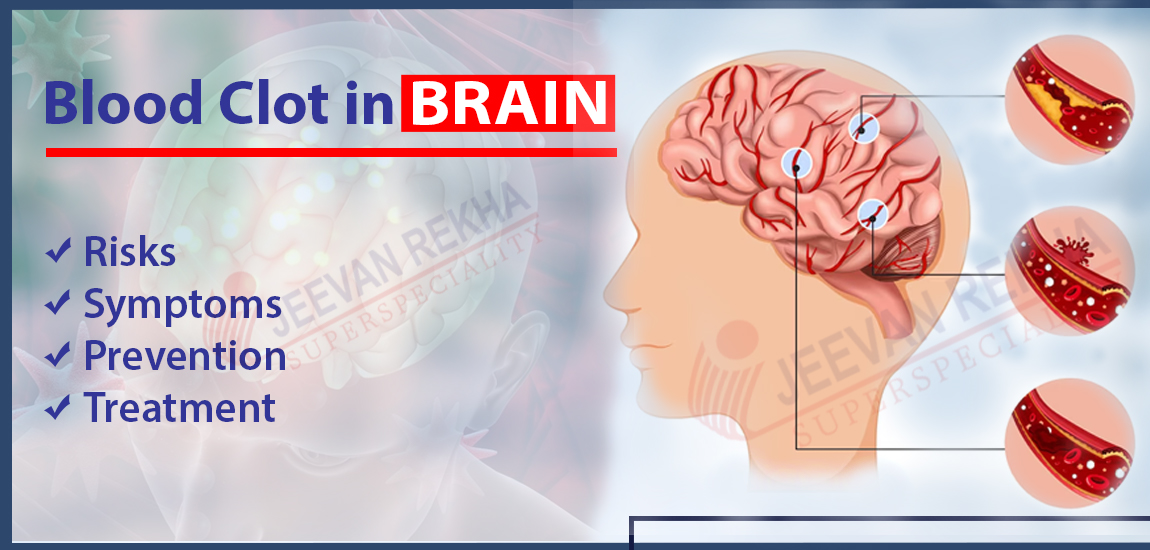
A blood clot in the brain, known medically as cerebral embolism or thrombosis, occurs when a blockage forms in an artery or vein that provides blood to the brain or within the brain itself.
When such a clot develops, it obstructs the normal flow of blood, which is crucial for delivering oxygen and nutrients to brain cells. This interruption in blood flow can lead to serious consequences such as tissue damage or even the death of brain cells, known as a stroke.
The presence of a blood clot in the brain requires urgent medical attention to prevent further complications and mitigate potential long-term effects on brain function.
Symptoms of Blood Clot in Brain
Symptoms of a blood clot in the brain can vary depending on factors such as the location and size of the clot. Common symptoms may include sudden onset of:
- Severe headache: Often described as the worst headache ever experienced, especially if it appears suddenly without any known cause.
- Weakness or paralysis: Typically affecting one side of the body, which may include the face, arm, or leg. This weakness or paralysis may come on suddenly or progress gradually.
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech: Sudden confusion, slurred speech, or difficulty finding the right words.
- Vision problems: Sudden onset of blurred or double vision, loss of vision in one or both eyes, or difficulty seeing in one or both eyes.
- Dizziness: Sudden onset of dizziness, loss of coordination, or difficulty walking.
- Seizures: In some cases, a blood clot in the brain may trigger seizures, which can vary in severity.
- Nausea: Especially when accompanied by other neurological symptoms.
Causes of Blood Clot in Brain
The causes of a blood clot in the brain can vary, but they generally involve conditions that lead to the formation of clots within the blood vessels supplying the brain. Some common causes include:
- Atherosclerosis: This is a condition where the arteries become narrowed and hardened due to the buildup of fatty deposits (plaques). These plaques can rupture, leading to the formation of a clot that can block blood flow to the brain.
- Atrial Fibrillation: A heart rhythm disorder where the heart's upper chambers (atria) beat irregularly and rapidly, which can lead to the formation of blood clots that may travel to the brain.
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): Elevated blood pressure can damage blood vessel walls and promote the formation of clots.
- Smoking: Smoking harms blood vessels and elevates the likelihood of forming blood clots.
- Diabetes: Diabetes can damage blood vessels over time, increasing the risk of clots.
- High Cholesterol: Elevated levels of cholesterol can contribute to the buildup of plaques in the arteries, which may lead to clot formation.
- Certain Medical Conditions: Such as certain autoimmune disorders, genetic clotting disorders, or inflammatory conditions that can increase clotting risk.
- Surgery or Trauma: Especially if it involves the head or neck, which can predispose to clot formation.
How to Diagnosis Blood Clot in Brain?
Diagnosing a blood clot in the brain typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and imaging tests. Here's how it is usually diagnosed:
1. Medical History and Physical Examination:
- The doctor will ask about the symptoms you are experiencing, when they started, and any relevant medical history (such as previous strokes, heart conditions, or risk factors for clotting).
- A neurological examination will be conducted to assess strength, coordination, reflexes, and sensory function.
2. Imaging Tests:
- CT Scan (Computed Tomography): This is often the first imaging test done to assess if there is bleeding or a clot in the brain. It can quickly detect abnormalities in brain tissue.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): This provides more detailed images of the brain and can help differentiate between different types of strokes or identify smaller clots.
3. Blood Tests:
- Blood tests may be done to check for factors that can increase the risk of clotting, such as levels of clotting factors, cholesterol levels, or genetic factors that predispose to clot formation.
4. Other Tests:
- Angiography: This involves injecting a contrast dye into the blood vessels and taking X-ray images (angiogram) to visualize the blood flow in the brain and detect any blockages or abnormalities.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): This may be performed to check for irregular heart rhythms (like atrial fibrillation) that could increase the risk of clots traveling to the brain.
Read also: Difference Between Heart Failure and Heart Attack
Treatment of Blood Clot in Brain
The treatment of a blood clot in the brain, also known as a stroke due to ischemic causes (where a clot blocks blood flow), typically involves urgent medical intervention to restore blood flow to the affected part of the brain and prevent further damage. Here are the main approaches to treatment:
- Clot-busting Medications (Thrombolytics): Medications such as tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) may be administered intravenously to dissolve the clot and restore blood flow to the brain. This treatment is most effective when given within a few hours of the onset of symptoms, so it's crucial to seek medical help immediately.
- Mechanical Thrombectomy: In some cases, especially when the clot is large or located in a critical area of the brain, a procedure called mechanical thrombectomy may be performed. This involves inserting a catheter into the blood vessel to physically remove or break up the clot, often using a device like a stent retriever.
- Anticoagulant or Antiplatelet Medications: After the acute phase of treatment, medications such as aspirin, clopidogrel, or other anticoagulants may be prescribed to prevent further clot formation and reduce the risk of future strokes.
- Management of Underlying Conditions: Treating underlying conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes, or high cholesterol is crucial to reduce the risk of future clot formation.
- Rehabilitation and Supportive Care: Rehabilitation therapies, including physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy, may be needed to help regain lost functions and improve recovery. Supportive care to manage complications such as swallowing difficulties, infections, or complications related to immobility may also be necessary.
- Monitoring and Follow-up: Close monitoring in a hospital setting initially and then through outpatient visits is essential to assess recovery progress, manage medications, and address any new symptoms or complications.
Conclusion
At Jeevan Rekha Hospital, we prioritize swift and effective treatment for patients experiencing a blood clot in the brain, a condition that demands urgent medical attention for neurology care.
Our specialized team is dedicated to providing timely diagnosis through advanced imaging techniques and initiating appropriate therapies such as clot-busting medications or mechanical thrombectomy when necessary.
We emphasize comprehensive care, including rehabilitation and management of underlying health conditions, to optimize recovery and reduce the risk of future complications. With a commitment to patient-centered care and ongoing support, Jeevan Rekha Hospital strives to ensure the best possible outcomes for every individual affected by this critical condition.
Tags
Blog Search
Latest Posts
-
Ear Infections (Otitis Media): Top Triggers & How to Avoid Them?
April 11, 2025 -
Implantation Bleeding Vs Periods: Know the Difference
March 12, 2025 -
5 Tips for a Happy and Healthy Summer
February 27, 2025 -
Body Ache (Pain): Causes, Symptoms and Treatment Options
February 10, 2025 -
Fatigue and Exhaustion: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
January 08, 2025




